News detail
Zircon mullite bricks – Applications in glass kilns
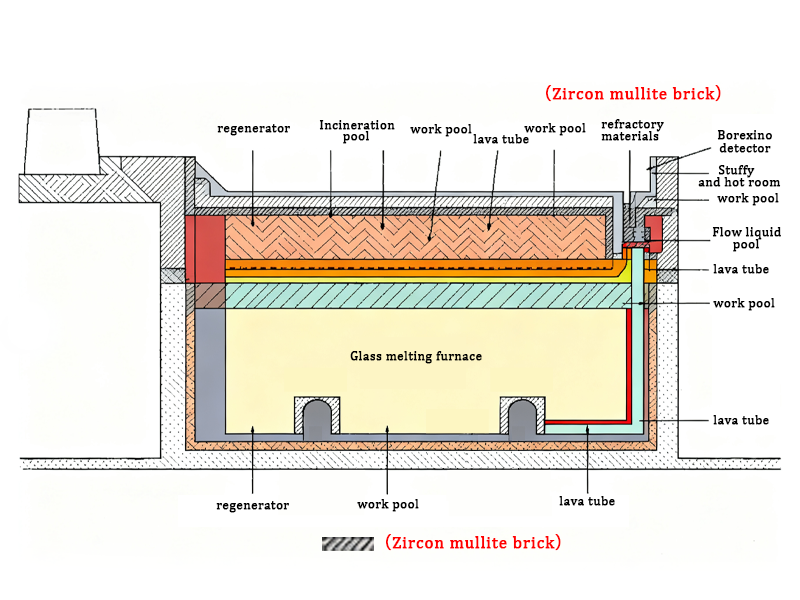
- Regenerator Chamber Grid Structure
Operating Conditions and Brick Applications
The regenerator chamber is the “waste heat recovery station” of the glass kiln. It alternately absorbs heat from the flue gas and heats the combustion air through a grid structure (mostly composed of stacked checker bricks). The operating conditions are characterized by frequent temperature fluctuations (500-1400℃) and erosion from dust and sulfides in the flue gas. Zircon mullite bricks are mainly used for constructing the grid structure in the medium- and high-temperature zones, especially in large float glass kiln regenerator chambers, often replacing traditional high-alumina bricks or silica bricks as the core grid material.
Core Functions
Strong Thermal Shock Resistance: It can withstand frequent temperature changes, preventing the grid structure from cracking or collapsing due to thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring the long-term stability of the regenerator structure.
Excellent Erosion Resistance: It can resist the erosion of acidic substances and dust in the flue gas, reducing grid blockage, maintaining waste heat recovery efficiency, and reducing kiln energy consumption. - L-shaped Nose Area of the Wall-Mounted Structure
Location and Application of Bricks
The L-shaped nose area of the wall-mounted structure is located at a turning point in the glass furnace body (such as the “corner” connecting the melting and cooling sections). It is a stress concentration zone, subjected to both radiation from the flame above (temperatures above 1400℃) and erosion from the volatiles of molten glass below. It also needs to withstand the weight of the wall itself and the tensile force generated by thermal expansion. Zircon mullite bricks, due to their balanced mechanical properties and erosion resistance, are specifically used for constructing the wall-mounted structure in this area, especially in the “load-bearing section” and “erosion section” of the nose area.
Core Functions
Load Bearing and Deformation Resistance: Possessing high compressive strength at both room and high temperatures, it can withstand structural stress, preventing bending and detachment of the wall-mounted structure in the nose area due to uneven stress.
Dual Erosion Resistance: Resistant to sintering deformation caused by high-temperature flame radiation and erosion by alkali metal oxides from molten glass, avoiding the risk of leakage caused by brick peeling.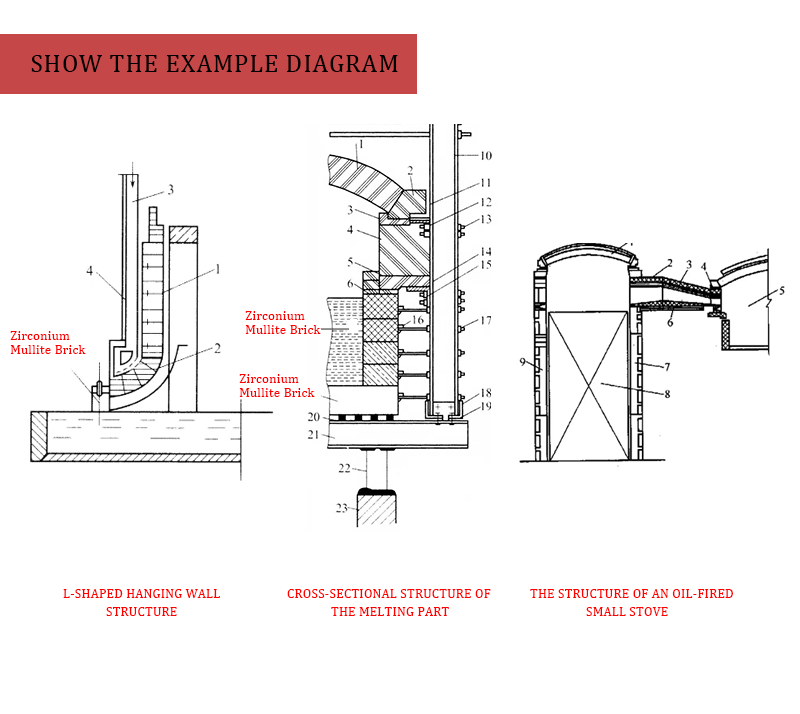
- Melting Section
Operating Conditions and Brick Application
The melting section is the “core production area” of the glass furnace. Raw materials such as quartz sand are heated to 1500-1600℃ and melted into molten glass. The operating conditions are characterized by prolonged high temperatures, direct erosion by the molten glass, and chemical corrosion from volatile raw materials (such as alkali metals and borides). Zircon mullite bricks are mainly used in the bottom and lower part of the melting section (the “liquidline zone” near the molten glass surface), and are a key lining material for the melting section of large float glass furnaces.
Core Functions
High Temperature Stability: Maintains a stable crystal structure even at 1600℃, without softening or sintering shrinkage, preventing deformation of the bottom/walls that could lead to molten glass leakage.
Resistance to Molten Glass Erosion: The zircon component in the brick forms stable compounds with the alkali metals in the molten glass, reducing the dissolution and erosion of the brick by the molten glass, extending the furnace life of the melting section, and preventing impurities from the brick from incorporating into the molten glass and affecting product quality. - Small-Scale Kilns
Application of Bricks in Different Parts and Operating Conditions
Small-scale kilns (such as laboratory glass melting furnaces, small art glass kilns, and special glass pilot furnaces) are characterized by their small volume, variable operating conditions (e.g., rapid temperature rise and fall, flexible raw material types), and frequent start-ups and shutdowns. This places higher demands on the adaptability and durability of the bricks used. Zircon mullite bricks can be used in key parts of small-scale kilns, such as the furnace lining, furnace bottom, and furnace door, and are particularly suitable for firing special glasses requiring high purity (such as optical glass and microcrystalline glass).
Core Functions
Adaptability to Frequent Start-ups and Shutdowns: Excellent thermal shock resistance can cope with frequent temperature fluctuations in small-scale kilns, reducing brick cracking and lowering maintenance costs.
Ensuring Glass Purity: The bricks have low impurity content and are resistant to erosion from raw material volatiles, preventing brick components from migrating into the molten glass and ensuring the stable quality of special glass produced in small-scale kilns.


Send inquiry
Please Leave your message you want to know! We will respond to your inquiry within 24 hours!